Optimal Respiratory Ranges: A Guide To Healthy Breathing
What exactly is meant by "normal respiratory range"?
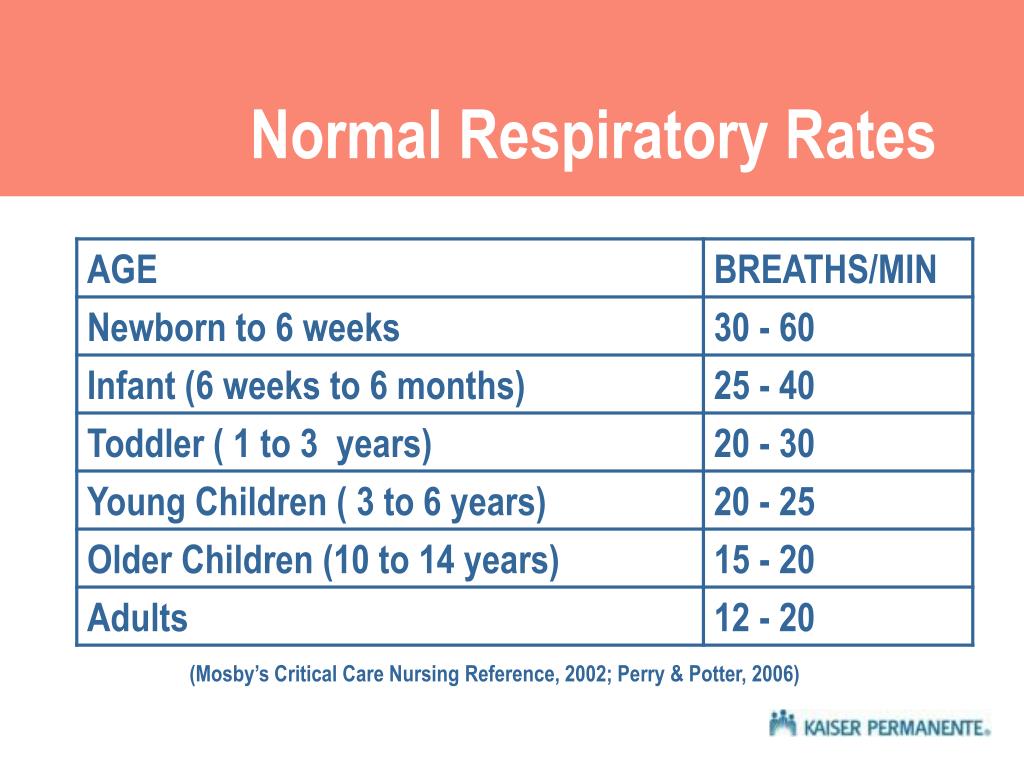
The normal respiratory range refers to the typical number of breaths a person takes per minute when they are at rest. This range can vary depending on a person's age, sex, and level of physical activity. However, the average normal respiratory rate for adults is between 12 and 16 breaths per minute.
Maintaining a normal respiratory rate is important for overall health. The respiratory system is responsible for taking in oxygen and expelling carbon dioxide. When the respiratory rate is too slow or too fast, the body may not be able to get enough oxygen or expel enough carbon dioxide. This can lead to a variety of health problems, including shortness of breath, fatigue, and confusion.
Read also:Discover The Number Of Children Marlo Thomas And Phil Donahue Welcomed
There are a number of factors that can affect the respiratory rate. These include:
- Age: The respiratory rate tends to be higher in children than in adults. This is because children have smaller lungs and a faster metabolism.
- Sex: The respiratory rate is typically higher in women than in men. This is because women have smaller lungs than men.
- Level of physical activity: The respiratory rate increases during physical activity. This is because the body needs more oxygen to fuel the muscles.
- Certain medical conditions: Some medical conditions, such as asthma and COPD, can affect the respiratory rate.
If you are concerned about your respiratory rate, it is important to talk to your doctor. They can help you determine if your respiratory rate is normal and, if not, what steps you can take to improve it.
Normal Respiratory Range
Key Aspects
- The normal respiratory rate for adults is between 12 and 16 breaths per minute.
- The respiratory rate can be affected by age, sex, and level of physical activity.
- Maintaining a normal respiratory rate is important for overall health.
Factors Affecting Respiratory Rate
- Age
- Sex
- Level of physical activity
- Certain medical conditions
Health Implications of Abnormal Respiratory Rate
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue
- Confusion
Conclusion
The normal respiratory range is an important indicator of overall health. By understanding the factors that can affect the respiratory rate, you can help to maintain a healthy respiratory system.
Normal Respiratory Range
The normal respiratory range refers to the typical number of breaths a person takes per minute when they are at rest. This range can vary depending on a person's age, sex, and level of physical activity. However, the average normal respiratory rate for adults is between 12 and 16 breaths per minute.
- Age: The respiratory rate tends to be higher in children than in adults.
- Sex: The respiratory rate is typically higher in women than in men.
- Physical activity: The respiratory rate increases during physical activity.
- Medical conditions: Some medical conditions, such as asthma and COPD, can affect the respiratory rate.
- Sleep: The respiratory rate typically decreases during sleep.
Maintaining a normal respiratory rate is important for overall health. The respiratory system is responsible for taking in oxygen and expelling carbon dioxide. When the respiratory rate is too slow or too fast, the body may not be able to get enough oxygen or expel enough carbon dioxide. This can lead to a variety of health problems, including shortness of breath, fatigue, and confusion.
If you are concerned about your respiratory rate, it is important to talk to your doctor. They can help you determine if your respiratory rate is normal and, if not, what steps you can take to improve it.
Read also:Experience Ultimate Fitness With Vasa Fitness In Tulsa
Age
The respiratory rate is the number of breaths a person takes per minute. The normal respiratory rate for adults is between 12 and 16 breaths per minute. However, the respiratory rate is typically higher in children than in adults. This is because children have smaller lungs and a faster metabolism.
- Facet 1: Smaller lungs
Children have smaller lungs than adults. This means that they have less space to store air. As a result, they need to breathe more often to get the same amount of oxygen. - Facet 2: Faster metabolism
Children have a faster metabolism than adults. This means that their bodies burn through energy more quickly. As a result, they need to breathe more often to get the oxygen they need to fuel their bodies.
The higher respiratory rate in children is normal and healthy. However, if a child's respiratory rate is significantly higher than normal, it could be a sign of an underlying medical condition. If you are concerned about your child's respiratory rate, it is important to talk to a doctor.
Sex
The normal respiratory rate for adults is between 12 and 16 breaths per minute. However, the respiratory rate is typically higher in women than in men. This is due to a number of factors, including:
- Facet 1: Smaller lungs
Women have smaller lungs than men. This means that they have less space to store air. As a result, they need to breathe more often to get the same amount of oxygen. - Facet 2: Faster metabolism
Women have a faster metabolism than men. This means that their bodies burn through energy more quickly. As a result, they need to breathe more often to get the oxygen they need to fuel their bodies. - Facet 3: Hormonal changes
Women's respiratory rates can also be affected by hormonal changes, such as those that occur during pregnancy and menopause.
The higher respiratory rate in women is normal and healthy. However, if a woman's respiratory rate is significantly higher than normal, it could be a sign of an underlying medical condition. If you are concerned about your respiratory rate, it is important to talk to a doctor.
Physical activity
The respiratory rate is the number of breaths a person takes per minute. The normal respiratory rate for adults is between 12 and 16 breaths per minute. However, the respiratory rate increases during physical activity. This is because the body needs more oxygen to fuel the muscles. The increased oxygen demand is met by increasing the respiratory rate and depth of breathing.
The increase in respiratory rate during physical activity is a normal and healthy response. However, if a person's respiratory rate is significantly higher than normal during physical activity, it could be a sign of an underlying medical condition. If you are concerned about your respiratory rate during physical activity, it is important to talk to a doctor.
The connection between physical activity and respiratory rate is important to understand because it can help people to optimize their health and fitness. By understanding how the respiratory rate changes during physical activity, people can adjust their exercise intensity and duration to achieve their fitness goals.
Medical conditions
Certain medical conditions can have a significant impact on the respiratory rate. Two common conditions that can affect the respiratory rate are asthma and COPD (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease).
- Facet 1: Asthma
Asthma is a chronic condition that causes inflammation and narrowing of the airways. This can make it difficult to breathe, leading to symptoms such as wheezing, coughing, and shortness of breath. Asthma can also cause the respiratory rate to increase, as the body tries to compensate for the difficulty breathing. - Facet 2: COPD
COPD is a group of lung diseases that cause airflow blockage and difficulty breathing. COPD can also cause the respiratory rate to increase, as the body tries to compensate for the difficulty breathing.
It is important to note that the respiratory rate can also be affected by other medical conditions, such as pneumonia, heart failure, and obesity. If you are concerned about your respiratory rate, it is important to talk to a doctor to determine if there is an underlying medical condition that needs to be treated.
Sleep
The respiratory rate, or the number of breaths a person takes per minute, typically decreases during sleep. This is because the body's metabolism slows down during sleep, and less oxygen is needed. The normal respiratory rate for adults is between 12 and 16 breaths per minute, but it may decrease to as low as 10 breaths per minute during sleep.
- Facet 1: Decreased oxygen demand
During sleep, the body's metabolism slows down, and less oxygen is needed. This is because the body is not actively engaged in physical activity or other tasks that require a lot of energy. As a result, the respiratory rate decreases to match the decreased oxygen demand. - Facet 2: Relaxation of the respiratory muscles
During sleep, the muscles in the body, including the respiratory muscles, relax. This relaxation can lead to a decrease in the respiratory rate. Additionally, the airways may also relax during sleep, which can further decrease the respiratory rate. - Facet 3: Hormonal changes
Hormonal changes that occur during sleep may also play a role in decreasing the respiratory rate. For example, the hormone melatonin, which is released during sleep, has been shown to have a sedative effect on the respiratory system. - Facet 4: Sleep disorders
Certain sleep disorders, such as sleep apnea, can affect the respiratory rate during sleep. Sleep apnea is a condition in which a person stops breathing for short periods of time during sleep. This can lead to a decrease in the average respiratory rate during sleep.
The decrease in respiratory rate during sleep is a normal and healthy response to the body's decreased oxygen demand. However, if a person's respiratory rate decreases significantly during sleep, or if they experience other symptoms such as shortness of breath or fatigue, it is important to see a doctor to rule out any underlying medical conditions.
Frequently Asked Questions about Normal Respiratory Range
The normal respiratory range refers to the typical number of breaths a person takes per minute when they are at rest. This range can vary depending on a person's age, sex, and level of physical activity. However, the average normal respiratory rate for adults is between 12 and 16 breaths per minute.
Question 1: What is considered a normal respiratory rate?
The normal respiratory rate for adults is between 12 and 16 breaths per minute. However, the respiratory rate can vary depending on a person's age, sex, and level of physical activity.
Question 2: What can affect the respiratory rate?
The respiratory rate can be affected by a number of factors, including age, sex, level of physical activity, and certain medical conditions.
Summary:
The normal respiratory range is an important indicator of overall health. By understanding the factors that can affect the respiratory rate, you can help to maintain a healthy respiratory system.
Conclusion
The normal respiratory range is an important indicator of overall health. The respiratory system is responsible for taking in oxygen and expelling carbon dioxide. When the respiratory rate is too slow or too fast, the body may not be able to get enough oxygen or expel enough carbon dioxide. This can lead to a variety of health problems, including shortness of breath, fatigue, and confusion.
Maintaining a normal respiratory rate is important for overall health. By understanding the factors that can affect the respiratory rate, you can help to maintain a healthy respiratory system.
The Ultimate Guide To The Faces And Voices Of NSYNC
The Age Of Todd Gurley: Uncovering His Years
The Ultimate Guide To Johnny Carson's Wives: Past And Present

Respiratory Rate Chart By Age Ponasa
PPT Vital Signs in the Ambulatory Setting An EvidenceBased Approach
Clinical Practice Guidelines Normal Ranges for Physiological Variables