Discovering Colorado Brown Bears: A Fascinating Guide To Their Habitat And Lifestyle
Colorado brown bears are majestic creatures that roam the rugged landscapes of Colorado’s wilderness. These powerful animals are not only a symbol of strength but also an integral part of the state’s ecosystem. With their immense size, sharp claws, and keen sense of smell, these bears play a vital role in maintaining the balance of nature. Despite their imposing presence, Colorado brown bears are often misunderstood, and learning about their habits and habitats can help foster a deeper appreciation for these incredible animals. Whether you’re a wildlife enthusiast or simply curious about Colorado’s natural treasures, understanding the life of brown bears is both fascinating and rewarding.
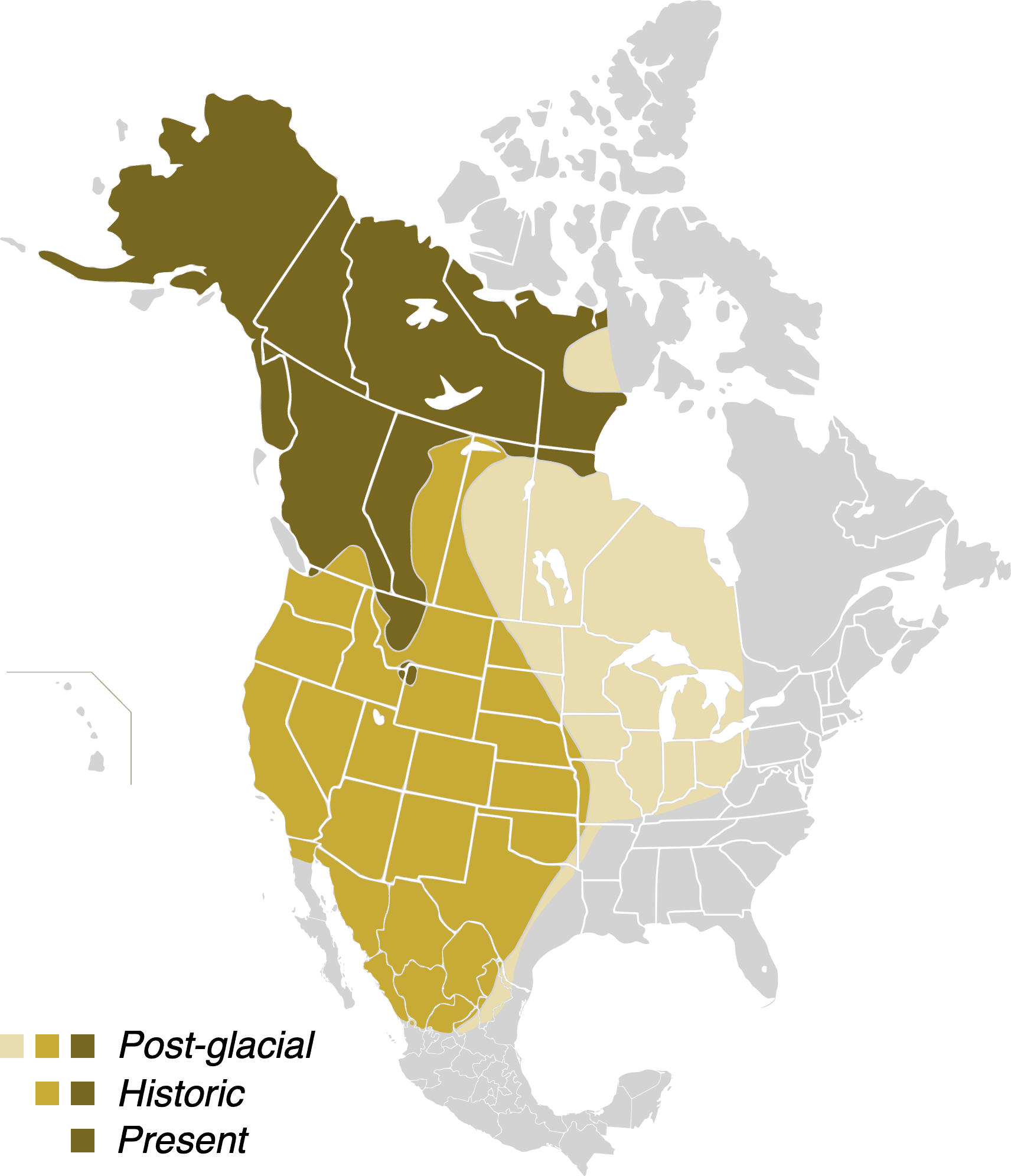
Colorado brown bears are primarily found in the mountainous regions of the state, where they thrive in dense forests and open meadows. Their adaptability to different environments makes them resilient survivors, capable of withstanding harsh winters and unpredictable weather patterns. These bears are omnivores, feeding on a diverse diet that includes berries, nuts, fish, and small mammals. Their ability to store fat during the summer and fall months ensures they can hibernate through the colder seasons, emerging in spring ready to explore and forage once again. This adaptability and resourcefulness are what make Colorado brown bears such a captivating species to study.
While Colorado brown bears are a rare sight due to their elusive nature, their presence is felt throughout the state’s wilderness. Conservation efforts have been instrumental in protecting their habitats and ensuring their survival. Understanding the challenges they face, such as habitat loss and human encroachment, is crucial to preserving these magnificent animals for future generations. By exploring their behavior, diet, and conservation status, we can gain a deeper insight into the lives of Colorado brown bears and the vital role they play in Colorado’s natural heritage.
Read also:Get The Latest News From Kate Bolduan On Cnn
Table of Contents
- What Do Colorado Brown Bears Eat?
- Why Are Colorado Brown Bears Important to the Ecosystem?
- How Do Colorado Brown Bears Adapt to Seasonal Changes?
- Where Can You Spot Colorado Brown Bears in the Wild?
- What Are the Threats to Colorado Brown Bears?
- How Can We Contribute to Colorado Brown Bear Conservation?
- What Makes Colorado Brown Bears Different from Other Bear Species?
- Frequently Asked Questions About Colorado Brown Bears
What Do Colorado Brown Bears Eat?
Colorado brown bears are omnivores, which means their diet is incredibly diverse. They are opportunistic feeders, consuming a wide range of foods depending on the season and availability. During the spring and summer months, these bears feast on plant-based foods such as berries, nuts, and grasses. Berries, in particular, are a favorite, with huckleberries and serviceberries being common choices. These foods provide the bears with essential nutrients and help them build up fat reserves for the winter months.
In addition to plant-based foods, Colorado brown bears also consume animal protein. They are skilled hunters and scavengers, often feeding on fish, small mammals, and carrion. Streams and rivers teeming with fish, such as salmon or trout, are prime hunting grounds for these bears. Their sharp claws and powerful jaws make them efficient predators, capable of catching fast-moving prey. Interestingly, Colorado brown bears are also known to dig up insects, such as ants and beetles, which provide a rich source of protein.
The fall season is particularly critical for Colorado brown bears as they enter a phase known as hyperphagia. During this time, they consume vast quantities of food to prepare for hibernation. Their diet shifts to calorie-dense foods like acorns and honey, which help them pack on the pounds necessary to survive the winter. Understanding what Colorado brown bears eat not only highlights their adaptability but also underscores the importance of preserving their natural habitats to ensure a steady food supply.
Key Components of a Colorado Brown Bear's Diet
- Berries (huckleberries, serviceberries)
- Nuts (acorns)
- Grasses and roots
- Fish (salmon, trout)
- Small mammals and carrion
- Insects (ants, beetles)
Why Are Colorado Brown Bears Important to the Ecosystem?
Colorado brown bears play a crucial role in maintaining the health and balance of their ecosystems. As apex predators and omnivores, they influence the populations of various species, both plant and animal. By preying on herbivores and scavenging carrion, they help regulate the populations of smaller animals, preventing overgrazing and ensuring the survival of plant species. This balance is essential for the overall health of the ecosystem.
One of the most fascinating ways Colorado brown bears contribute to their environment is through seed dispersal. When they consume berries and other fruits, the seeds pass through their digestive system and are deposited in different locations. This process helps plants spread and thrive, promoting biodiversity. Additionally, their foraging habits, such as digging for roots and insects, aerate the soil and enhance its fertility, benefiting other plant and animal species.
Colorado brown bears also serve as indicators of environmental health. Their presence or absence can signal changes in the ecosystem, such as habitat degradation or climate change. By studying these bears, scientists can gain valuable insights into the state of Colorado’s wilderness and identify potential threats to the environment. Protecting Colorado brown bears is not just about preserving a single species—it’s about safeguarding the intricate web of life that depends on them.
Read also:The Ultimate Melissa Mcbride Movie And Tv Show Guide
How Do Colorado Brown Bears Impact Plant and Animal Life?
The relationship between Colorado brown bears and their environment is a prime example of symbiosis. Their activities directly and indirectly benefit countless species. For instance, when bears dig for insects, they create small disturbances in the soil that can promote plant growth. Similarly, their predation on smaller animals helps maintain a balance that prevents any one species from dominating the ecosystem.
Examples of Symbiotic Relationships
- Bears and plants: Seed dispersal through berry consumption
- Bears and scavengers: Carrion sharing supports other predators
- Bears and soil health: Digging enhances soil fertility
How Do Colorado Brown Bears Adapt to Seasonal Changes?
Colorado brown bears are masters of adaptation, capable of thriving in a variety of environments and conditions. One of their most remarkable adaptations is hibernation, a process that allows them to survive the harsh winters when food is scarce. During the fall, they enter a phase called hyperphagia, during which they consume massive amounts of food to build up fat reserves. These reserves sustain them throughout the winter, during which they remain in a state of dormancy in their dens.
Hibernation is not just about sleeping; it’s a complex physiological process. Colorado brown bears lower their metabolic rate, heart rate, and body temperature to conserve energy. Despite this, they remain alert enough to care for their cubs if they are mothers. Female bears give birth during hibernation, and the cubs stay with their mother in the den until spring, relying on her milk for nourishment. This adaptation ensures the survival of the next generation, even in the harshest conditions.
During the warmer months, Colorado brown bears exhibit other adaptive behaviors. They are highly mobile, traveling long distances in search of food. Their keen sense of smell allows them to locate food sources from miles away, whether it’s a berry patch or a fish-filled stream. Their thick fur provides insulation against the cold, while their strong limbs and sharp claws enable them to climb, dig, and hunt effectively. These adaptations make Colorado brown bears one of the most resilient species in the animal kingdom.
What Role Does Hibernation Play in a Bear’s Life?
Hibernation is a critical survival strategy for Colorado brown bears, allowing them to endure long periods without food. It also plays a vital role in reproduction, as females give birth and nurse their cubs during this time. Understanding hibernation provides insight into the incredible resilience of these animals and highlights the importance of protecting their habitats.
Stages of Hibernation
- Hyperphagia: Building fat reserves
- Denning: Finding and preparing a safe den
- Dormancy: Lowering metabolic rate and conserving energy
- Emergence: Leaving the den in spring
Where Can You Spot Colorado Brown Bears in the Wild?
Colorado brown bears are elusive creatures, but with patience and the right knowledge, it’s possible to catch a glimpse of them in their natural habitat. These bears are primarily found in the mountainous regions of Colorado, including national parks like Rocky Mountain National Park and the San Juan Mountains. Dense forests, alpine meadows, and river valleys are their preferred environments, offering ample food sources and shelter.
One of the best times to spot Colorado brown bears is during the early morning or late evening when they are most active. They are often seen foraging for food near berry patches, streams, or areas with abundant vegetation. Wildlife enthusiasts should always maintain a safe distance and avoid disturbing the bears. Responsible wildlife viewing not only ensures your safety but also respects the animals’ natural behaviors.
If you’re planning a trip to see Colorado brown bears, consider joining a guided wildlife tour. These tours are led by experienced naturalists who can provide valuable insights into bear behavior and ecology. Additionally, they can help you identify the best spots for bear sightings while minimizing your impact on the environment. Whether you’re an avid photographer or simply a nature lover, observing Colorado brown bears in the wild is an unforgettable experience.
What Are the Best Practices for Observing Colorado Brown Bears?
When observing Colorado brown bears, it’s essential to follow ethical guidelines to ensure both your safety and the bears’ well-being. Always use binoculars or a zoom lens to view them from a distance, and never attempt to approach or feed them. Bears are wild animals, and approaching them can lead to dangerous situations.
Tips for Safe Wildlife Viewing
- Stay at least 100 yards away from bears
- Use binoculars or a camera with a zoom lens
- Travel in groups and make noise to avoid surprising bears
- Store food securely to prevent attracting bears
What Are the Threats to Colorado Brown Bears?
Despite their resilience, Colorado brown bears face numerous threats that endanger their survival. Habitat loss is one of the most significant challenges, driven by urbanization, logging, and agricultural expansion. As human populations grow, bears are increasingly forced into smaller and fragmented habitats, limiting their access to food and increasing the likelihood of human-wildlife conflicts.
Climate change is another pressing issue affecting Colorado brown bears. Rising temperatures and changing precipitation patterns can disrupt the availability of food sources, such as berries and fish. This can lead to malnutrition and reduced reproductive success, further threatening their populations. Additionally, climate change can alter hibernation patterns, making it harder for bears to adapt to new conditions.
Human activities, such as poaching and vehicle collisions, also pose significant risks to Colorado brown bears. While conservation laws are in place to protect these animals, illegal hunting and accidental deaths remain a concern. Educating the public about the importance of coexisting with wildlife is crucial to reducing these threats and ensuring the long-term survival of Colorado brown bears.
How Does Climate Change Affect Colorado Brown Bears?
Climate change has far-reaching effects on Colorado brown bears, from altering their food sources to disrupting their hibernation cycles. Understanding these impacts is essential for developing effective conservation strategies and mitigating the effects of a changing climate.
Effects of Climate Change on Bears
- Reduced availability of berries and nuts
- Changes in fish migration patterns
- Disrupted hibernation cycles
- Increased risk of habitat loss
How Can We Contribute to Colorado Brown Bear Conservation?
Conservation efforts are vital to protecting Colorado brown bears and ensuring their survival for future generations. One of the most effective ways to contribute is by supporting organizations dedicated to wildlife conservation. These organizations work to protect bear habitats, conduct research,
Discover The Magic Of Skating Rink Bellingham: Your Ultimate Guide
Fantasy Football Trash Talk: The Ultimate Guide To Dominating Your League
Precious Moments Musical Doll: The Ultimate Guide To Collecting And Cherishing
Do Grizzly Bears Still Live in Colorado? Uncover Colorado

Do Grizzly Bears Still Live in Colorado? Uncover Colorado